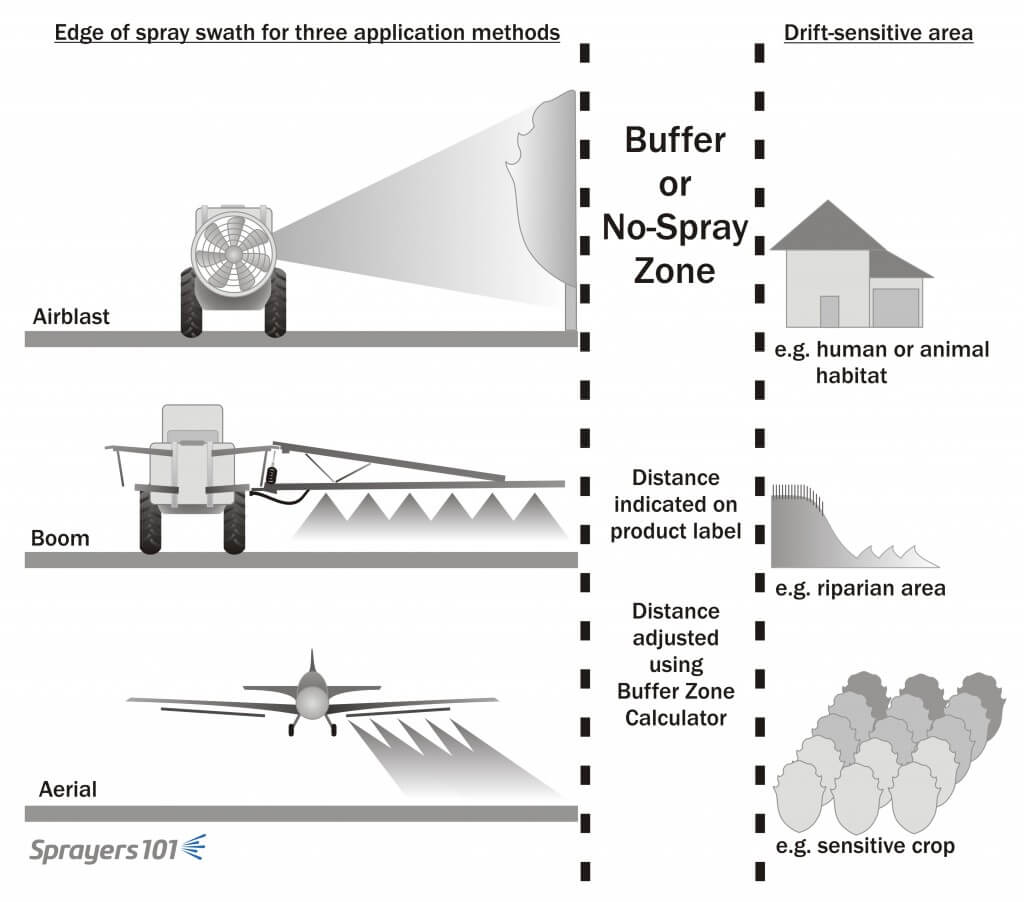
Spray Buffer Zones
Spray buffer zones are no-spray areas required at the time of application between the area being treated and the closest downwind edge of a sensitive terrestrial or aquatic habitat. Spray buffer zones reduce the amount of spray drift that enters downwind, non-target areas.
Sensitive Terrestrial Habitats
Sensitive terrestrial habitats can include hedgerows, grasslands, shelterbelts, windbreaks, forested areas and woodlots. Crops and private properties adjacent to treated areas are not considered to be sensitive terrestrial habitats and do not require spray buffer zones. However, labelled spray buffer zones are a good indicator of potential damage to adjacent vegetation. Applicators are responsible for ensuring their spraying programs do not adversely affect neighbouring properties.
Sensitive Aquatic Habitats
Sensitive aquatic habitats can include lakes, rivers, streams (channelized or natural), creeks, reservoirs, marshes, wetlands and ponds. Temporary bodies of water resulting from flooding or drainage to low-lying areas are not considered sensitive aquatic habitats. Nor are aquatic drainage ditches or seasonal water courses that are dry at the time of application. Water body depth will determine the buffer zone distance, as indicated on the pesticide label. Downslope open water may also require a vegetative filter strip .
The pesticide label will indicate when a spray buffer zone is required. The distance will depend on the product used, the method of application and the crop being sprayed. In some cases, the buffer zone may be modified using Health Canada’s Spray Buffer Zone Calculator . When provincial and label restrictions differ, or label restrictions differ between tank mix partners, use the greatest distance.
Spray Buffer Zone Calculator
Unless forbidden by the pesticide label, Health Canada’s Spray Buffer Zone Calculator may permit applicators to reduce the size of the spray buffer zone specified on a pesticide label. To be eligible, the product label must specify a field or aerial spray quality coarser than “Very Fine” and finer than “Very Coarse”. All airblast spray qualities are applicable.
Modifications are based on meteorological conditions, sprayer configuration and the application method at the time of application. If modified spray buffer zone distances are less than provincial or municipal distances, use the greater distance.
Applicators that choose to use the calculator must retain a copy of the summary page for at least one year following the application to demonstrate compliance with label directions.
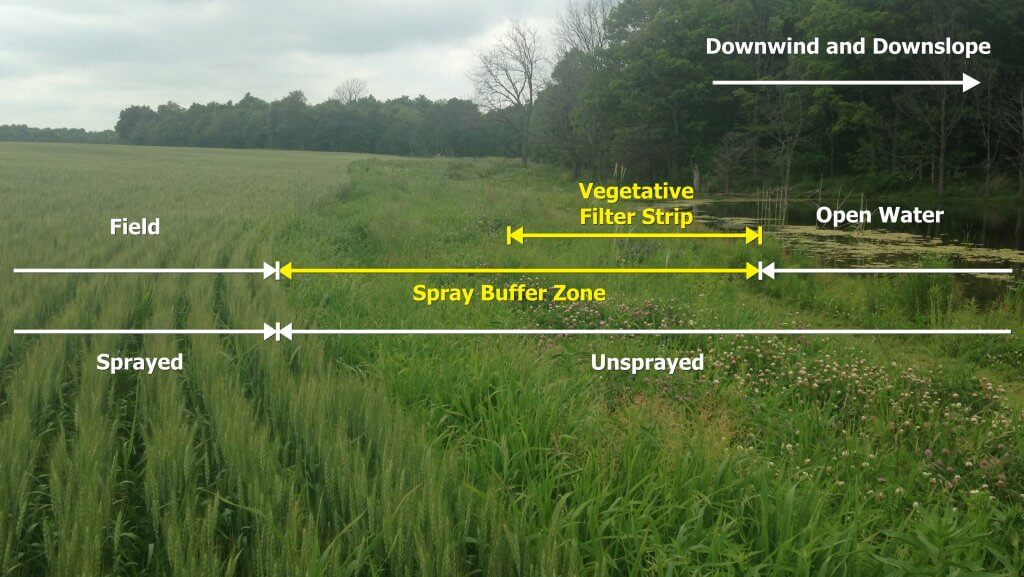
Vegetative Filter Strips
A vegetative filter strip is a permanently vegetated strip of land that sits between an agricultural field and downslope surface waters. Vegetative filter strips reduce the amount of pesticide entering surface waters from runoff by slowing runoff water and filtering out pesticides carried with the runoff.
Pesticide labels may require a vegetative filter strip, or recommend one, as a best management practice. They must be at least 10 metres wide from edge of field to the surface water body and be composed primarily, but not exclusively, of grasses.
Spray buffer zones do not apply to vegetative filter strips unless there is a pre-existing sensitive terrestrial habitat within them. Therefore, vegetative filter strips may overlap spray buffer zones when open water is both downslope and downwind (see illustration). In this case, the minimum 10 metres vegetative filter strip distance must be observed, but the set-back can be larger based on spray buffer zone, provincial or municipal restrictions.
Soil Fumigant Buffer Zones
Soil Fumigant Buffer Zones are mandatory, untreated perimeters surrounding the treated field. They limit user exposure and increase the protection of workers, bystanders and the environment. The distance will depend on the application method, product rate and field size, as indicated on the pesticide label. An Emergency Response Plan is required when residences or businesses are located within 90 metres of the buffer zone perimeter.
Soil fumigant buffer zones have a time component. This Buffer Zone Period begins at the start of the application and ends a minimum 48 hours following the application. Respiratory protection and stop-work triggers, as specified on the pesticide label, will apply to anyone present in the buffer zone area during the buffer zone period.
Buildings and residential areas within the soil fumigant buffer zone must be unoccupied during this period. Unless in transit, non-handlers (including field workers) must be excluded from the soil fumigant buffer zone during this period. Entry is permitted for fumigant handlers with appropriate certification, emergency personnel and local, provincial, or federal officials performing inspection, sampling, or other similar duties.

Soil fumigant buffer zone signage must be posted within 24 hours prior to the application and remain posted until the buffer zone period expires. Signage must include, but is not limited to, the date and time the buffer zone period ends and the name, address, and telephone number of the applicator. Soil fumigant buffer zone signage must be located at the outer perimeter of the buffer zone, at all entrances to the field, and along likely routes where people not under the owner’s control may approach. Soil fumigant buffer zone signs are in addition to, and do not replace, fumigant application block signage .
Applicators must develop a written Fumigation Management Plan prior to the start of any application. The plan outlines key steps to ensure a safe and effective fumigation, including site conditions, buffer zones and emergency response planning. Both the owner/operator of the fumigated area and the fumigant applicator must retain signed fumigant management plans as well as a summary of Post-Application Procedures for two years following the application.
