The calibration of handheld plot sprayers is an important part of agricultural research, and this article already covers all the bases… as long as you are spraying broadacre or row crops. But what happens when you are trying to emulate an airblast sprayer and treating a tree, bush, cane or vine?
The key difference is that spraying a two dimensional area requires the operator to pass the boom over the target at a uniform height and pace to achieve consistent coverage. But, a three-dimensional target requires the operator to circle the target, or spray from both sides, until it has received the required dose (or volume).
In order to scale down a typical airblast carrier volume for small plot work, we need to know three things:
- The area you wish to treat (e.g. bush, grape panel, tree, etc.), including it’s share of the alley (in m2).
- The emission rate from the calibrated plot sprayer (in US gal./min.)
- The airblast carrier volume you wish to scale down (e.g. L/ha).
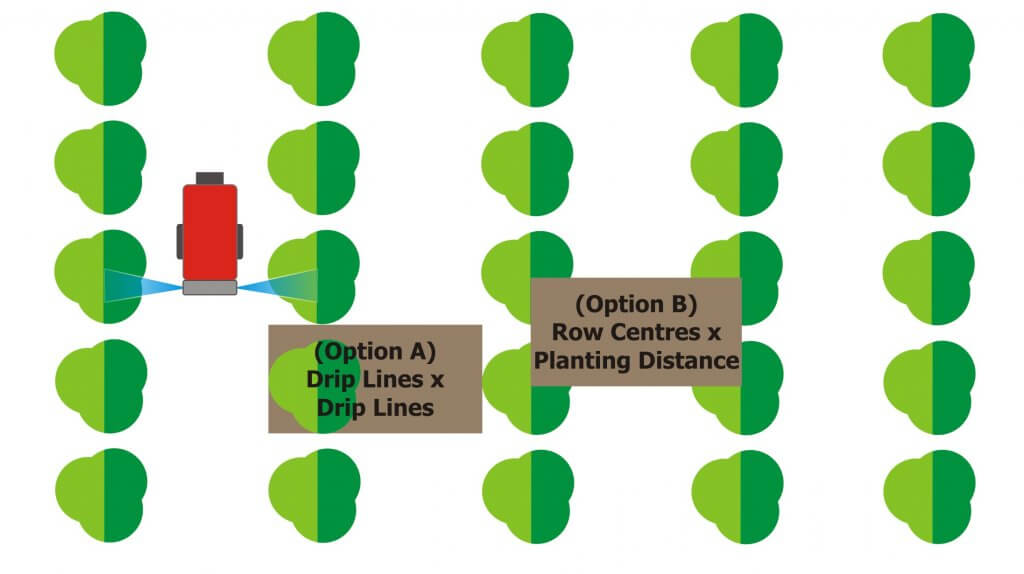
The illustration below shows two options for calculating the treated area. Option A requires you to measure from the outermost edges of the canopy (imagine if the canopy was wet and dripping – the dripline is that outermost point). It is less consistent than the preferred Option B, where the area is determined from row centres and planting distance.

If you are using a CO2 powered hand wand (preferred over a manual pump) with one or more hydraulic nozzles, then you can calibrate it using the methods in this article. There are battery-powered options from Jacto and Petra Tools, the latter offering a battery powered ULV system as well. Makita also has a battery entry (image below). However, if you are using a backpack mistblower, which better approximates an airblast sprayer compared to a hydraulic hand boom (see this article), it requires a different approach. Plus, you get to look like a Ghostbuster, which is a win in my book.

Follow along in the following images as we explore how to calibrate a backpack step by step:




Be aware that most mistblowers use gravity to feed the spray mix from the tank to the boom. A pressure pump kit is recommended for applications where the spray tube is held upward more than 30 degrees to maintain a consistent discharge rate. A hip belt is also recommended to reduce fatigue. Examples are shown below are for Stihl-brand sprayers. Some may or may not require the pump (e.g. Tomahawk) but they are primarily intended for mosquito control and in that case a consistent rate over a vertical plane may not be as important.

If your sprayer does not have a pump kit, pointing the boom upward will cause spray to slow or even stop. This greatly diminishes your ability to reach high targets and achieve consistent coverage. In this case, attach the deflector (which comes with the sprayer) before proceeding with the calibration.

Set the flow rate to the preferred setting (usually a dial at the end of the boom), and using a stopwatch, time how long it takes to spray the entire volume. Be sure to move the boom exactly as you would when spraying the target, either side-to-side or up-and-down, to capture possible rate changes from the gravity feed. Convert the output to US gal./min.

Alternately, some people will stand on a bathroom scale with the backpack full. Then get off and spray for a period of time. Then get back on the scale. One millilitre of water weighs one gram, so you can calculate the flow from the weight difference.
Now you know the area and the emission rate. You should have a target carrier volume in mind (e.g. L/ha). Using the following example, let’s determine how long you need to spray the target:
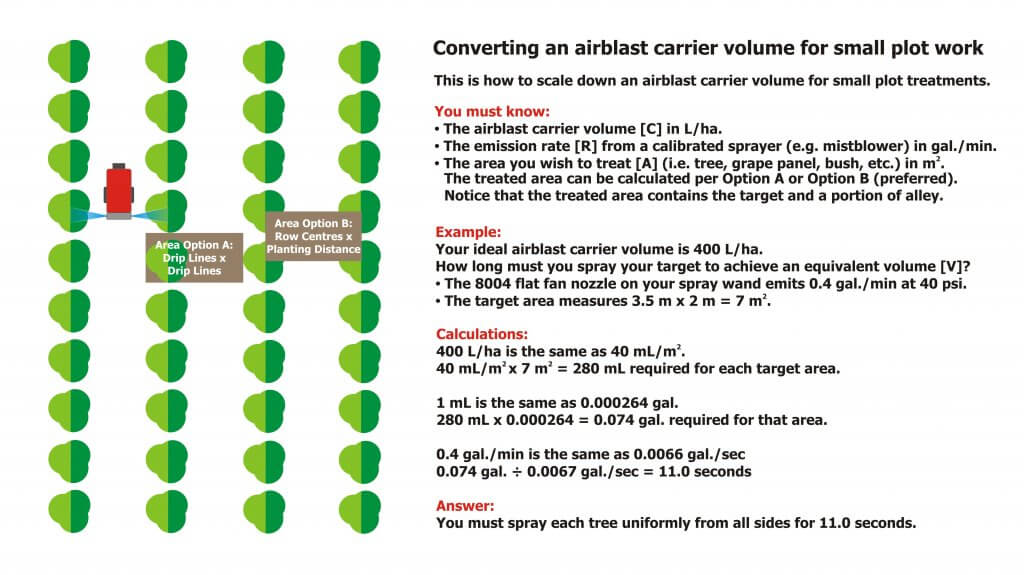
In this example, an ideal airblast Carrier Volume [C] for the orchard is 400 L/ha. We want to scale this down to determine the Volume for Treated Area [V]. First, divide [C] by 100 to convert it to 40 mL/m2. Then, because in Canada our nozzles are in US units, we do an ugly conversion: Since 1 mL = 0.000264 US gallons, [C] becomes 0.0106 US gal./m2.
The Treated Area [A] measures 3.5 m by 2 m = 7 m2.
The Emission Rate [R] is the rate the plot sprayer sprays. While we prefer using a mistblower, many still use a hand wand with no air assist. In this case let’s suppose we are using a hand wand with two 8002 flat fan nozzles operating at 40 psi. According to our calibration, we confirm it sprays 0.4 US gal./min.
- [C](US gal./m2) × [A](m2) = [V] (US gal.)
- 0.0106 US gal./m2 × 7 m2 = 0.074 US gal.

We know we want to spray the target with 0.074 US gal., and we also know [R] which says our boom emits 0.4 US gal./min. We convert this to seconds by dividing by 60, so [R] = 0.0067 US gal./sec. From this we can calculate how long [T] we must spray the target.
- [V](US gal.) / [R](US gal./sec.) = [T](seconds).
- 0.074 US gal. / 0.0067 US gal./sec. = approximately 11.0 seconds.
So, we know that to spray the target with an equivalent 400 L/ha, we must achieve consistent coverage from all sides by spraying it for a total of 11 seconds. Pro tip: Always mix a little more spray volume than you will need to account for priming.
This is only one way to calibrate a backpack sprayer for spot spraying. If it’s isn’t quite what you need, check out these resources:
- Calibrating a Knapsack Sprayer (www.weedfree.co.uk – 2008)
- Don’t Overlook Backpack Sprayers (John Grande, Rutgers)
- Hand Sprayer Calibration Steps Worksheet (Bob Wolf, Kansas State University – 2010)
- Sprayer Calibration Using the 1/128th Method for Motorized Backpack Mist Sprayer Systems (Jensen Uyeda et al., University of Hawai’i – 2015)
