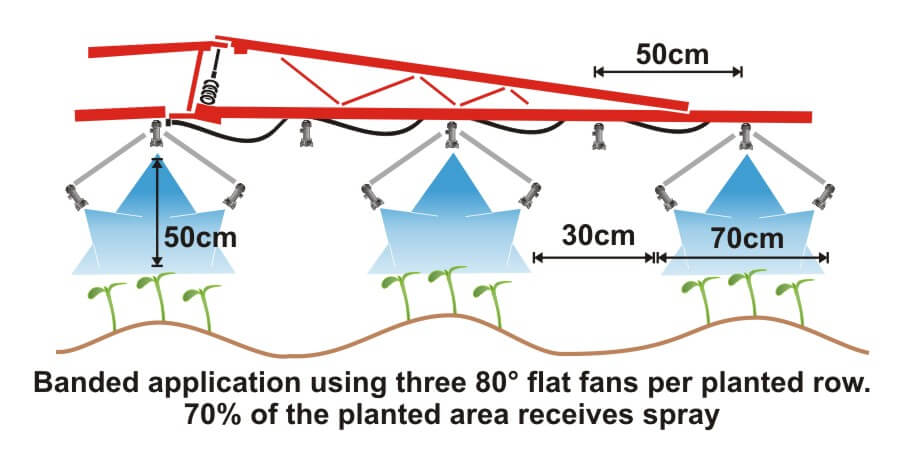
Originally published in: Wolf, T.M. and Downer, R.A. ILASS Americas, 11th Annual Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Sacramento, CA, May, 1998 Note to reader: It’s been nearly 23 years since we wrote this paper at the invitation of organizers of the Institute for Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems Conference. At the time, custom […]
Read More… from Developing Criteria for the Ideal Agricultural Spray – a Biologist’s Perspective